La Nina weather phenomenon: Knowing the effects in Indonesia.
Kehidupan di perantauan • 5 November 2024
The La Niña weather phenomenon, characterized by a reduction of temperature or cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean, has been anticipated to exert its influence on weather patterns worldwide. El Niño and La Niña are opposite phases of the weather phenomenon known as the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO). When La Niña occurs, the weather effects are opposite to those of El Niño.
Impacts of La Nina
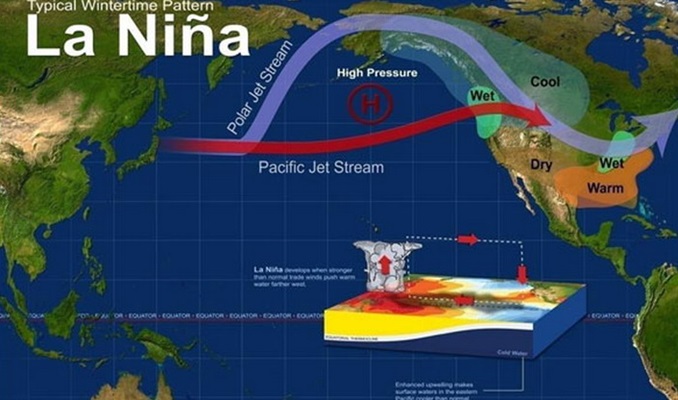
La Niña typically brings wetter-than-average conditions to the Pacific Northwest and the northern United States, while the southern United States may face drier and warmer weather. In South America, La Niña often results in above-average rainfall in northern regions, contrasting with drier conditions in southern areas. Across the Asia-Pacific and Africa regions, impacts vary, with increased rainfall expected in parts of Southeast Asia and Australia, while other areas may experience reduced precipitation. Its impacts extend beyond weather phenomena and affect various socioeconomic sectors, including agriculture, water management, energy demand, and commodity markets.
Is Indonesia affected?
La Niña brings increased rainfall to most parts of Indonesia and slightly lower temperatures across the country. This increased rainfall can benefit agriculture by replenishing water reservoirs and improving soil moisture. However, excessive rainfall can lead to flooding, landslides, and waterlogging, causing significant damage to crops, infrastructure, and livelihoods.
The La Nina phenomenon, which is predicted to occur from mid-to-this year, has the potential to increase rainfall and significantly impact agriculture in Indonesia.
Mitigating the issue
Affected countries like Indonesia are urged to increase Investments in irrigation infrastructure, water storage facilities, and drainage systems, which can help regulate water supply and reduce the risk of water-related disasters. Farming specialists are also advising for diversification of crop production so it can enhance resilience to La Niña-induced weather variability. Farmers can explore drought-resistant crop varieties, shift planting schedules, and adopt agroforestry and intercropping practices to improve soil health and water retention
Improve weather forecasting capabilities is essential for enabling farmers and policymakers to anticipate La Niña’s onset and prepare accordingly.


